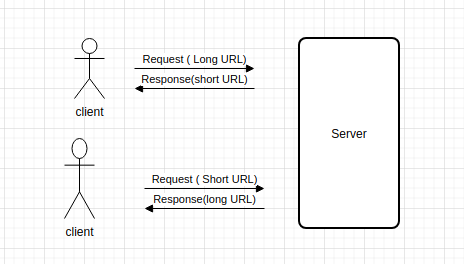
URLs for a job post, google map, and Amazon products are really long and not human readable.
1. Gather Functional Requirements
User's view of the system (use cases)
unpack the vague problem and ask clarifying questions.
shows that you can communicat
Functional Requirements:
1. Given long URL, return a short URL
2. Given a short URL, send back a long URL
3*.If the same long URLs are requested, return a different short URLs.
(ex. Influencer marketing) (Other people want to use the long URL)
Optional Functional Requirements:
a. Customized URL
b. Retention Policy for Long URL and Short URL
c. Analytics (how many clicks for the short URL)
2. Cluster the functional requirements into a collection of microservicesIn this URL shortener case, it requires a simple data and architectural requirement. SKIP
3. Draw the logical architectural diagram
Draw and explain the data/logic flow between microservices
Microservices with data modeling
Request: POST tinyurl.com/longurl
Response: {shortURL}
Request: Get tinyURL.com/shorturl
response: {longurl}
Key-Value pair: ShortURL:longURL
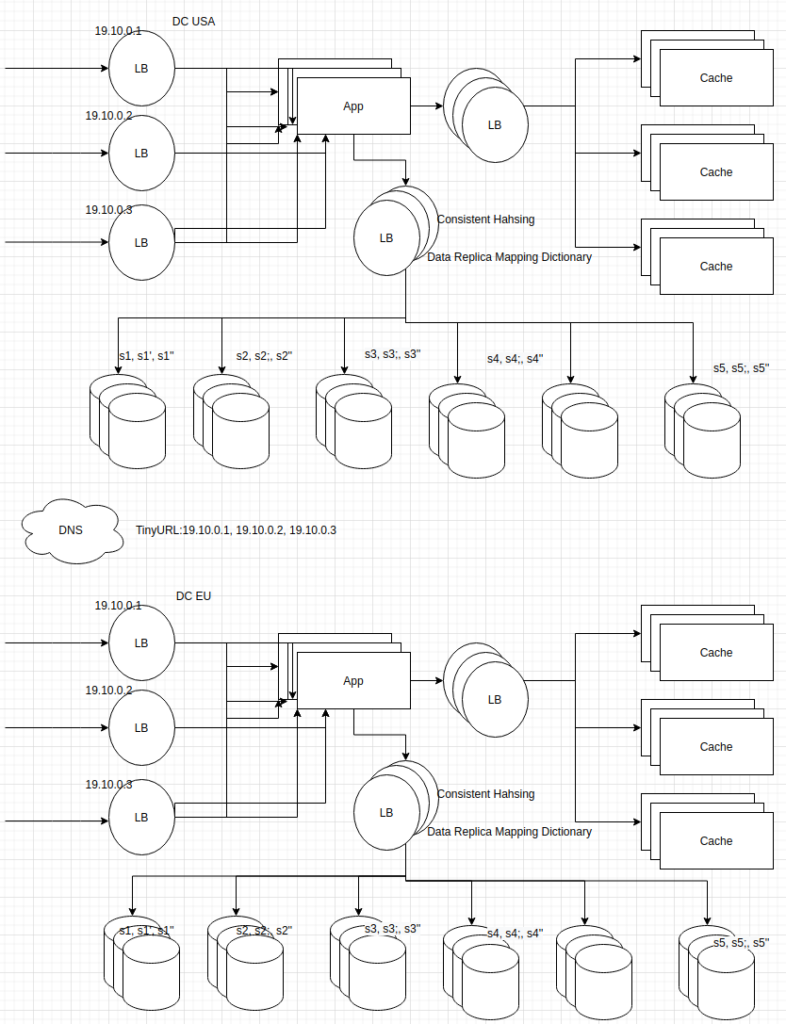
4. Deep dive into each microserviceOption 1. Counter method. 0, 1, 2, 3, .. , 999999
6 bytes characters can have 10**7-1 Short URLs. Not enough short URLs.
BASE64={0: ‘0’, 1: ‘1’, 2: ‘2’, 3: ‘3’, 4: ‘4’, 5: ‘5’, 6: ‘6’, 7: ‘7’, 8: ‘8’, 9: ‘9’, 10: ‘a’, 11: ‘b’, 12: ‘c’, 13: ‘d’, 14: ‘e’, 15: ‘f’, 16: ‘g’, 17: ‘h’, 18: ‘i’, 19: ‘j’, 20: ‘k’, 21: ‘l’, 22: ‘m’, 23: ‘n’, 24: ‘o’, 25: ‘p’, 26: ‘q’, 27: ‘r’, 28: ‘s’, 29: ‘t’, 30: ‘u’, 31: ‘v’, 32: ‘w’, 33: ‘x’, 34: ‘y’, 35: ‘z’, 36: ‘A’, 37: ‘B’, 38: ‘C’, 39: ‘D’, 40: ‘E’, 41: ‘F’, 42: ‘G’, 43: ‘H’, 44: ‘I’, 45: ‘J’, 46: ‘K’, 47: ‘L’, 48: ‘M’, 49: ‘N’, 50: ‘O’, 51: ‘P’, 52: ‘Q’, 53: ‘R’, 54: ‘S’, 55: ‘T’, 56: ‘U’, 57: ‘V’, 58: ‘W’, 59: ‘X’, 60: ‘Y’, 61: ‘Z’, 62: ‘_’, 63: ‘-‘}
counter = 999999 ==> 3Q8- : shortedned 6 chars to 4 chars
def encode(n):
num64 = []
while n:
n, rem = divmod(n, 64)
num64.append(base64[rem])
num64.reverse()
return num64
Option2. hash.md5(timestamp + long URL) because the same long URL need to server the different short URLs
import hashlib
from datetime import datetime
bits128 = hashlib.md5(“http://stackoverflow.com/212121”.encode()+ascii(datetime.now().timestamp())).digest()
Use 6 bits (BASE64) *6 = 36 bits out of 128 bits ==> 64**7 -1 = 4398046511103
Option 3. Pregenerate the short UTL offline because the short URL does not depend on the long URL.
5. Check for Scalabilities
Reasons for scaling the distributed system
- Size of Data
- Throughput QPS (query per seconds) > maximum Capacity
- Response time > 500 ms ? Yellow sign
- Availability/Reliability
- Geo Location
- Hot Spots ( Celebrities in SNS, Metropolitans in Maps )
1. Calculating Estimated data Size for short URLs
100 queries per seconds (create)
100*100 queries per seconds (read)
3 years = 3*365*24*60*60 = 94608000 ~= 100,000,000 = 100x10^6
longURL=(2kB) + shortURL:(6B*6=36B) ~= 2KB
2Bx10^3*100X10^6 = 200Bx10^9 = 0.2x10^12 = 0.2 TB*100 = 20 TB
Commodity Machine = 128GB RAM and 2 TB Hard Disk
For 3 years data : 20TB
Hard Disk : 10 commodity Machine needed. (2TB x10)
Cached target 98% hit rates (20% of 20TB): 20TB *20% = 4TB = 31.25 ~= 32 commodity machines
90% hit rates => 10% of 20TB: 20TB*10%: 2TB: 15.6 ~= 16 commodity machines
All data storage: 10 Data Servers
90% hit rates: 16 cache servers
Replicas is 3x: 30 data servers, 48 cache servers
2. Calculating Throughput
Create: 100 QPS
Read: 100x100 QPS
Estimated time consumed by its service
APP: 1 ms
Cache: 2 ms
DB: 10 ms
App Thread can handle 1000 RPS
Cache thread can handle 500 RPS
DB thread can handle 100 RPS
Commodity Machine 12 cores and 8 threads = 96 threads per machine.
30% utilization of CPU for the APP.
APP: 0.3*96*1000 ~= 30000 Requests Machine/Second
Cache: 0.3*96*500 ~=15000 Requests Machine/Second
DB: 0.3*96*100 ~= 300 Requests Machine/Second
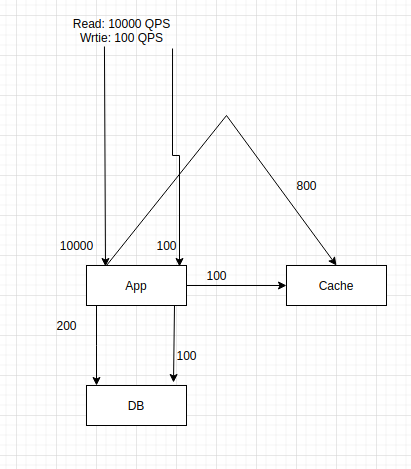
App needs to handle 10100 QPS: APP Machine can handle 30000 RPS for machine
Cache needs to handles 900 QPS: Cache Machine can handle 15000 RPS for machine
DB needs to handle 300 QPS: DB server can handle 300 RPS for machine
No needs for throughput scalability for App, Cache, and DB.
3. Response Time
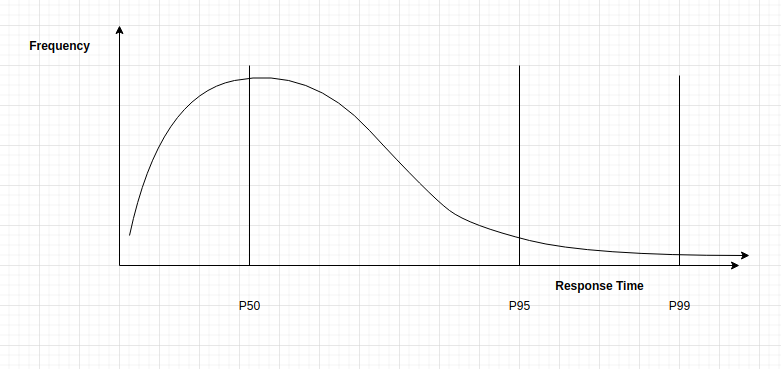
SLI indicates P50 < 200 ms, P99 < 1 sec and Availability >= 99.9%
Respinse Time = Latency (2Way RTT) + Service Time
Latency (Network Delay) = Transmission Time + Propagation Delay + queueing Delay
Transmission Time = Size/BandWidth
Propagation Delay = distance/ speed Of light
Queuing Delay => every Router has queue for enqueuing and dequeuing
Bandwidth = 200 Mbps = 25M B/S
If you want to download 2GB image, It will take 80 Secs
Maximum propagation Delay is The Earth Circumference/speed of light = 40000x10^3/2x10^8 = 200 ms.
If Service time take more than 500 ms, it need to save some 100 ms for reducing propagation delay for response time. But URL shortener service returns simplly a long URL with the response to a short URL. It would take for service time.
It would not need to consider a response time.In the case that the service time take longer, it may be consider geolocation in order to save some of propagation delay (100 ms ~150 ms save)